Repository mirroring from digitalocean repo to other git platforms
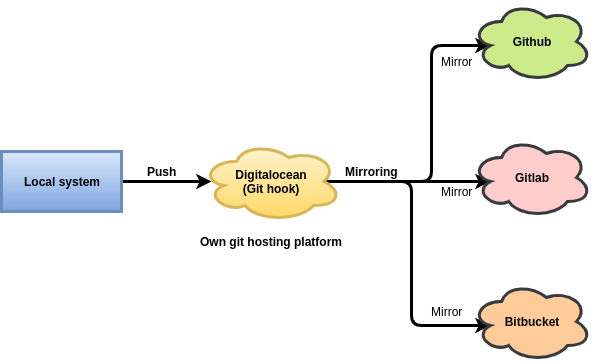
Share on:Edit on:Github, Gitlab, Bitbucker or any other code hosting platforms are great for hosting websites, apps or any other software. Each platform has it’s own large user base. It would be great if our code base is in sync across all emerging platforms. I have seen some great software already doing this. For example Linux kernel has it’s own git repository hosting at https://git.kernel.org/ and a mirror exists on Github.
I am going to use digitalocean droplet as my own git hosting platform. Whenever you see digitalocean droplet in this article, it means our own git hosting platform.
Refer the official documentation for setting up digitalocean droplet and taking SSH into it. After that, add an user with sudo permissions.
Step 1 : Create –bare repository on digitalocean droplet
Login using SSH to digitalocean droplet with new user account.
ssh username@droplet_ip_addr # ex: ssh pi@206.189.134.23
You can start an empty –bare repository or clone an existing repository.
To start an empty repository, use the following command. Replace REPO_NAME with any name you wanted. I am using website.git.
mkdir REPO_NAME && cd REPO_NAME && git init --bare
To clone an existing repository, use git clone –bare option.
git clone --bare https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
For example, I am cloning my existing repository from the Github to digitalocean droplet.
git clone --bare https://github.com/itsnayabsd/website.git
The –bare option allows this repo to receive/send push operations from/to remote repositories.
Step 2 : Create empty repositories on the hosting platforms
Create empty repo on Gitlab
Visit https://gitlab.com/ and create an empty repository and note down the repo URL. It looks something like this.
https://gitlab.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
ex: https://gitlab.com/itsnayabsd/website.git
Create empty repo on Github
Visit https://github.com/ and create an empty repository. The repo URL looks like following.
https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
ex: https://github.com/itsnayabsd/website.git
Create empty repo on Bitbucket
Visit https://bitbucket.org/ and create an empty repository. The repo URL looks like this.
https://USERNAME@bitbucket.org/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
ex: https://nayabbashasayed@bitbucket.org/nayabbashasayed/website.git
Step 3 : Add remote URLs to digitalocean droplet
Login using SSH to digitalocean droplet with new user account.
ssh username@droplet_ip_addr # ex: ssh pi@206.189.134.23
Change directory to the –bare repository you have created in step 1. In my case,
cd /home/pi/website.git
Add remote server URLs created in the step 2 to current repository with the following commands. Replace USERNAME and REPOSITORY with yours.
git remote add github_repo https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
git remote add gitlab_repo https://gitlab.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
git remote add bitbucket_repo https://USERNAME@bitbucket.org/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
Step 4 : Add git credentials for remote servers
Create .netrc file in the home directory and add the following content.
vi ~/.netrc
machine github.com
login USERNAME
password PASSWORD
machine gitlab.com
login USERNAME
password PASSWORD
machine bitbucket.org
login USERNAME
password PASSWORD
Replace USERNAME and PASSWORD with the respective git platform username and password.
Step 5 : Add a git hook on the remote server
Create post-receive file in the hooks directory.
vi hooks/post-receive
And add the following content to that file. Do not forget the first line #!/bin/sh.
#!/bin/sh
git --git-dir=/REPO_PATH_DIGITALOCEAN push -f github_repo master
git --git-dir=/REPO_PATH_DIGITALOCEAN push -f gitlab_repo master
git --git-dir=/REPO_PATH_DIGITALOCEAN push -f bitbucket_repo master
My post_receive file content is below
#!/bin/sh
git --git-dir=/home/pi/website.git push -f github_repo master
git --git-dir=/home/pi/website.git push -f gitlab_repo master
git --git-dir=/home/pi/website.git push -f bitbucket_repo master
Make this file executable
chmod +x hooks/post-receive
Step 6 : Cloning the digitalocean repo to local system.
Clone the repo created in Step 1 to local laptop or desktop.
git clone ssh://DROPLET_USERNAME@DROPLET_IP_ADDR/REPO_PATH_DIGITALOCEAN
ex: git clone ssh://pi@206.189.134.23/home/pi/website.git
Step 7 : Test the setup
Go to cloned repository directory in your local system. ex: cd website.
Create a dummy file, commit and push
echo dummy > dummy
git add dummy
git commit -m "New file dummy"
git push origin master
This should push the commit to ditigalocean droplet which in turn pushes this commit to github, gitlab and bitbucket platforms.